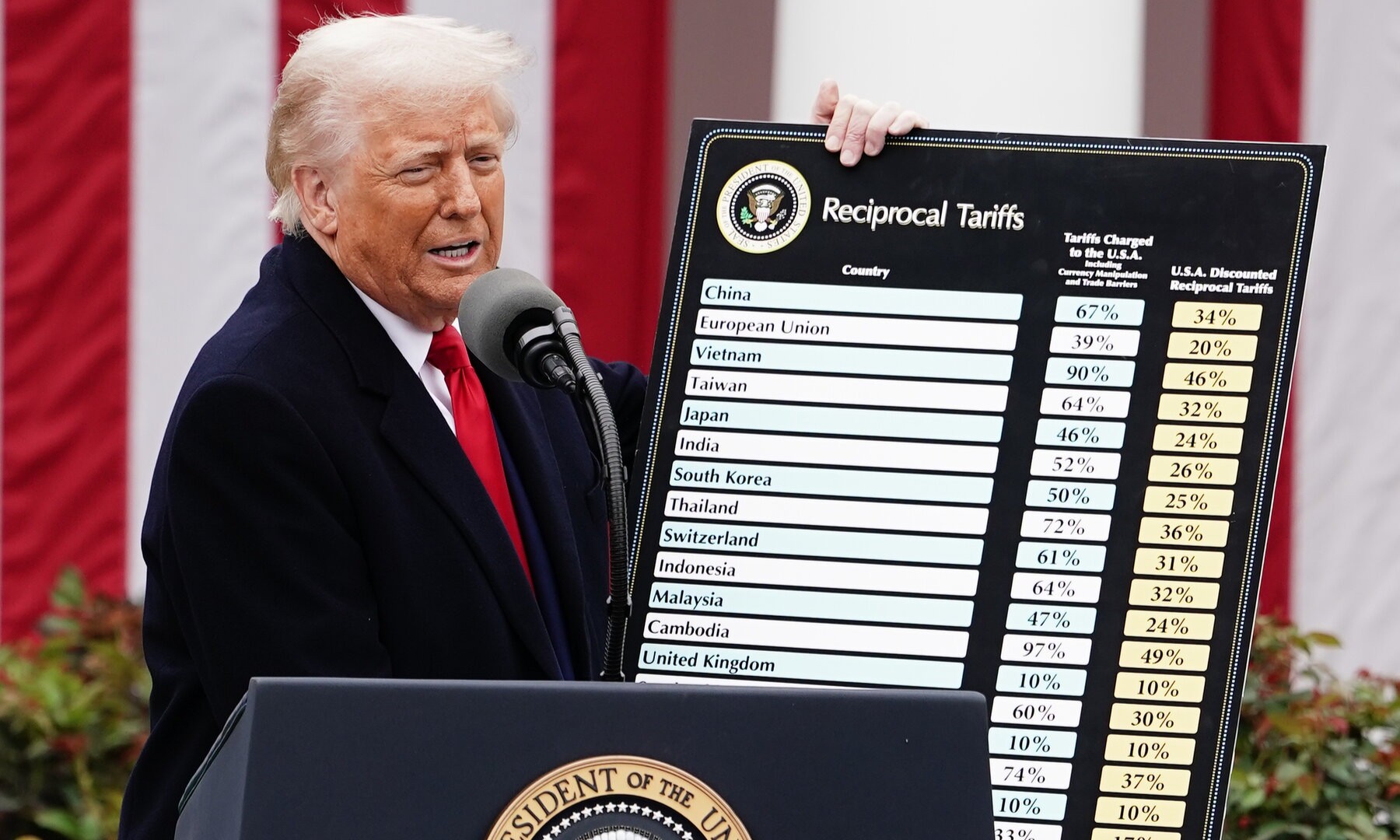
In 2025, President Donald Trump introduced a series of tariffs that had a significant impact on the global economy. These measures, aimed at reducing the US trade deficit, have set off chain reactions around the world, affecting markets, consumers and international relations.
Donald Trump’s tariff policies in 2025 have had significant repercussions on the global economy, triggering trade tensions, negatively impacting financial markets, and increasing costs for consumers and businesses. While the stated goal was to protect American industry and reduce the trade deficit, the side effects raised concerns about the long-term sustainability of such measures.
The Tariff Measures of the United States
In 2025, the United States significantly increased tariffs on imports from many countries, including China, as part of a strategy to reduce trade deficits and protect domestic industries. These measures have triggered reactions worldwide, including retaliatory tariffs from China and prepared countermeasures by the European Union. The trade tensions have affected global markets, economies, and international relations, raising concerns about the future of global trade. Below is a detailed overview of the U.S. tariffs, international responses, and their economic and political impacts.
April 2025: Market Crash and Immediate Reactions
On April 2, 2025, President Trump announced a 10% tariff on all imports, with increases up to 34% on goods from China and 20% on those from the European Union. These measures triggered an immediate negative reaction in the financial markets:
- On April 3, the Dow Jones fell by 1,679 points (−3.98%), while the S&P 500 dropped by 4.88% and the Nasdaq by 5.97%.
- On April 4, following Chinese retaliation with a 34% tariff on U.S. goods, the Dow Jones dropped another 2,231 points (−5.5%), the S&P 500 fell by 5.97%, and the Nasdaq by 5.8%, entering bear market territory.
- In total, during the two days following the tariff announcement, U.S. markets lost over $6.6 trillion in market value, marking the largest two-day market loss in history.
May 2025: Ongoing Instability and Economic Concerns
Despite a brief recovery at the end of April, markets continued to show volatility in May, influenced by further economic and political developments:
- On May 21, a weak auction of 20-year U.S. Treasury bonds raised concerns about the rising federal deficit. The yields on 30-year bonds rose to 5.089%, the highest level since 2023, reflecting investor skepticism about the market’s ability to absorb the growing public debt.
- On the same day, the Dow Jones lost 817 points (−1.9%), the S&P 500 declined 1.6%, and the Nasdaq fell 1.4%, with 10 of the 11 S&P sectors closing in the red.
- Retail sales showed signs of weakness: Target reported a decline in first-quarter sales and downgraded its outlook, attributing the situation to the impact of tariffs on consumers.
- Globally, concerns over U.S. debt and rising yields also affected Asian markets. Japan’s Nikkei fell 1.0%, Hong Kong’s Hang Seng dropped 0.9%, and South Korea’s Kospi declined 1.1%.
International reactions
In response, China imposed tariffs of 15% on US coal and liquefied natural gas, as well as 10% on oil, agricultural equipment and automobiles. Additionally, he filed a complaint with the World Trade Organization, accusing the United States of violating international trade rules. Imports from China were subject to a 34% tariff increase, bringing the total tariffs to 145%. This measure was justified by the White House as a response to the massive trade deficit with China, which amounted to approximately $295 billion in 2024.China: In retaliation, China imposed 125% tariffs on U.S. goods, including agricultural products like soybeans, pork, and beef. Additionally, China suspended imports of U.S. timber and added 11 U.S. entities to its “unreliable entities” list.
The EU had prepared tariff countermeasures on American goods worth 21 billion euros. However, following the announcement of the suspension by the United States, the EU decided to suspend the application of these countermeasures for 90 days, opening up the possibility of negotiations. ans
Impact on Italy
According to Codacons, US tariffs could lead to an increase in retail prices in Italy, with a hit of up to 4.2 billion euros on family spending.
The most affected sectors include automotive, food and mechanics. Italian companies could face additional costs of more than 4 billion to over 7 billion dollars, according to some simulations created by Prometeia
Food & Beverage Sector
- 25% Tariffs could result in a €2 billion loss in Italian food exports to the U.S., affecting key products like wine, olive oil, pasta, and cheese.
- Parmigiano Reggiano retail prices in the U.S. could rise from $50 to $59 per kg, reducing competitiveness.
- Italian wine may face a 20% tariff, causing an estimated annual loss of €323 million for the Italian wine industry.
Automotive Sector
- 25% U.S. tariffs on vehicles and components could raise car prices in Italy by up to €3,000, affecting popular models like Fiat Panda and VW T-Roc.
- Estimated job losses between 9,700 and 15,500 in the Italian auto industry, particularly among SMEs and subcontractors.
Other Sectors Affected
- Fashion & luxury: 10% tariffs could lead to €3 billion in export losses for Italian fashion brands.
- Machinery & electronics: Annual exports worth $11.8 billion could face an average 1.4% tariff increase, hurting Italy’s industrial competitiveness.
The information presented in this article are from a variety of national and international news including: Avvenire, Sky TG24, ANSA, Morning Star Italia, and Wikipedia etc. to ensure accurancy and reliability.